
208 or 480 Volt Service?
Posted by Joe Weagraff on in Engineering, Fundamentals
Selecting an electrical distribution voltage for a multi-tenant commercial building is often based on prior lease agreements, previous projects, incomplete information, or intuition. Our research provides guidelines with economic justifications.
Each type of service has its advantages. 208V requires less electrical equipment in the Tenant lease space and is therefore less expensive for the Tenant. 480V is lower in cost for the Landlord. It allows the use of smaller conductors from the utility transformer over greater distances as well as smaller Landlord distribution equipment―requiring less space for indoor electric rooms and offering more flexible truck dock loading space and Tenant door locations.
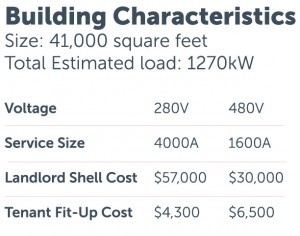
A careful evaluation of the building’s characteristics, including the size of the building, Tenant requirements, and anticipated loads, can help resolve any guesswork that was previously present in the service voltage determination. An example of this analysis follows:
- Number of tenants
- Overhead or underground service feed
- Distance to and location of the utility transformer
- Distance from Landlord service entrance to Tenant spaces
- The AIC rating of equipment and its effect on the downstream equipment
- Wireway or meter center
- With a 480/277V service, some of the Tenant’s branch circuit wire sizes are reduced (wire sizes for RTUs and number of lighting circuits) Building use: Restaurants and big box retailers prefer 480/277V, small retail, office, or residential Tenants prefer 208/120V
- Occasionally there are additional costs from the utility for using one voltage over the other
- In some instances the decision to have 208 power is solely at the discretion of the Utility

 Previous STORY
Previous STORY